You don't know polyfill
November 11, 2020
Babel은 ES6+ 코드를 ES5로 변환하는 도구이다. 이 문장만 읽으면 Babel이 polyfill과 동일한 개념이라고 오해할 수 있지만, Babel이 곧 polyfill을 의미하는 것은 아니다. ES5에 존재하지 않는 ES6의 메서드나 생성자는 지원하지 않기 때문이다.
예를 들어 Promise, Object.assign, Array.from 등은 ES5로 대체할 Syntax가 없기 때문에 변환되지 않는다.
// Yes! I can Do!
// Beforeconst helloBabel = () => {
return 'world';
}
// Aftervar helloBabel = function helloBabel() {
return 'world';
}
// No I can't
// Beforeconst helloPromise = new Promise(resolve => {
return resolve('world')
})
// Afterconst helloPromise = new Promise(resolve => {
return resolve('world')
})Promise 구문은 바뀌지 않았다. 이 코드는 ES6를 지원하지 않는 브라우저에서 에러가 발생한다.
이렇게 Babel이 변환할 수 없는 부분을 채우는 것이 바로 polyfill이다. 이 글에서는 babel과 polyfill.io에 대해 소개한다.
babel
babel@7.4.0 이전에는 @babel/polyfill을 많이 사용했지만 밑에서 소개할 문제로, 이제는 @babel/preset-env로 통합하여 사용한다.
⚠️ @babel/polyfill은 babel@7.4.0에서 deprecated 되었다.
@babel/polyfill
@babel/polyfill은 제너레이터 polyfillregenerator runtime과 ES5/6/7 polyfill인 core-js를 dependency로 가지고 있는 패키지이다.
// core-js@2.6.
// Cover all standardized ES6 APIs.
import "core-js/es6";
// Standard now
import "core-js/fn/array/includes";
import "core-js/fn/array/flat-map";
/* 생략 */
// Ensure that we polyfill ES6 compat for anything web-related, if it exists.
import "core-js/web";
import "regenerator-runtime/runtime";@babel/polyfill의 코드는 매우 간단하다. polyfill 모듈인 core-js와 regenerator-runtime을 import하는 역할만 한다.
core-js는 전역에 polyfill을 추가하기 전에 해당 기능이 있는지를 체크하기 때문에 최신 브라우저에서는 polyfill 없이 동작하게 되어 @babel/plugin-transform-runtime(corejs: false)를 사용하는 것에 비해 빠르다.
@babel/plugin-transform-runtime에서도
corejs: 2 | 3 | false를 적용할 수 있다. 이 내용은 하단에서 자세히 다룬다.
// https://github.com/zloirock/core-js/blob/v2/modules/_export.js
var $export = function (type, name, source) {
/* 생략 */
for (key in source) {
// contains in native own = !IS_FORCED && target && target[key] !== undefined;
// export native or passed
out = (own ? target : source)[key]; // bind timers to global for call from export context
exp = IS_BIND && own ? ctx(out, global) : IS_PROTO && typeof out == 'function' ? ctx(Function.call, out) : out;
// extend global
if (target) redefine(target, key, out, type & $export.U);
/* 생략 */
}
}@babel/polyfill에서 사용했던 core-js@2.6.5의 코드를 간단히 살펴보면, 전역 객체를 직접 수정하는 방식임을 알 수 있다.
// https://github.com/zloirock/core-js/blob/v2/modules/es7.array.includes.js
$export($export.P, 'Array', {
includes: function includes(el /* , fromIndex = 0 */) {
return $includes(this, el, arguments.length > 1 ? arguments[1] : undefined);
}
});전역 객체를 직접 수정하기 때문에 Array.prototype.includes 등 새로 추가된 프로토타입 메서드도 문제없이 사용 가능하고, 라이브러리가 어떤 프로토타입 메서드를 사용하는지 신경 쓸 필요가 없다.
하지만, @babel/polyfill에는 크게 두 가지 문제가 있다.
문제점 1
import "core-js/es6"
/* ...생략 */
import "regenerator-runtime/runtime";@babel/polyfill에서는 위와 같이 모듈을 import 하기 때문에, 사용하지 않는 polyfill도 번들에 포함되어 사이즈가 커진다. @babel/polyfill을 import 하는 순간, core-js es6/index.js 하위의 많은 모듈이 모두 번들에 포함되는 것이다.
문제점 2
@babel/polyfill은 딱 한번만 import해야 한다. 두 개 이상의 @babel/polyfill이 import되면 아래와 같은 오류가 발생한다.
🚨 Uncaught Error : only one instance of babel-polyfill is allowed내부에 global._babelPolyfill 이라는 전역 변수를 두고 2개 이상의 polyfill이 로드되면 에러를 발생하도록 해뒀다.
if (global._babelPolyfill && typeof console !== "undefined" && console.warn) {
console.warn(
"@babel/polyfill is loaded more than once on this page. This is probably not desirable/intended " +
/* ... */
);
}@babel/polyfill의 디펜던시인 core-js의 ES6/7 polyfill의 경우, 두 번 호출되면 내부적으로 오류가 발생되어 정상적으로 polyfill이 적용되지 않는다.
따라서 @babel/polyfill 이 두 번 호출되지 않도록 주의해야 한다.
@babel/plugin-transform-runtime
@babel/plugin-transform-runtime은 transpile 과정에서 polyfill이 필요한 부분의 동작을 내부 helper 함수로 치환하는 것이다. (관련 코드)
core-js를 peerDependency로 가지고 있고, alias 목록에 따라 전역 객체 수정 없이 내부 helper 함수로 치환하는 방식으로 polyfill이 적용 되도록 한다.
new Promise(resolve => resolve(1))위 코드는 transpile 과정을 거치면 다음과 같이 변한다. Promise 전역 객체를 직접 수정하지 않고 내부 객체를 생성하는 방식이다.
var _promise = require("babel-runtime/core-js/promise");
var _promise2 = _interopRequireDefault(_promise);
function _interopRequireDefault(obj) { return obj && obj.__esModule ? obj : { default: obj }; }
new _promise2.default(function (resolve) {
return resolve(1);
});Babel은 ES6+ 구문을 ES5로 치환하기 위해 여러 helper 함수들을 생성하는데, @babel/plugin-transform-runtime은 transpile 과정에서 이 helper 함수들이 다른 모듈을 참조하도록 변경한다.
class Circle {}@babel/plugin-transform-runtime이 없을 때는 아래와 같이 변환된다.
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) { //...
}
var Circle = function Circle() {
_classCallCheck(this, Circle);};class를 포함하는 모든 코드는 매번 _classCallCheck함수를 반복적으로 생성하게 된다.
@babel/plugin-transform-runtime을 사용하면 매번 helper 함수를 생성하지 않고 @babel/runtime, 혹은 corejs를 참조하는 방식으로 변경된다.
var _classCallCheck2 = require("@babel/runtime/helpers/classCallCheck");
var _classCallCheck3 = _interopRequireDefault(_classCallCheck2);
function _interopRequireDefault(obj) {
return obj && obj.__esModule ? obj : { default: obj };
}
var Person = function Person() { (0, _classCallCheck3.default)(this, Person);
};어떤 모듈을 참조할지는 corejs 옵션 값에 따라 달라지는데, 기본 값 false로 적용될 경우 @babel/runtime을 참조한다. (코드)
const moduleName = injectCoreJS3 // corejs === 3 ?
? "@babel/runtime-corejs3"
: injectCoreJS2 // corejs === 2 ?
? "@babel/runtime-corejs2"
: "@babel/runtime";
this.addDefaultImport(
`${modulePath}/${helpersDir}/${name}`,
name,
blockHoist,
);
// `${modulePath}/${helpersDir}/${name}` example:
// @babel/runtime/helpers/esm/${toArray}.js이 방식을 사용할 땐 한 가지 주의할 점이 있다.
예를 들어, axios를 디펜던시로 사용하는 프로젝트에서는 node_modules/axios까지 transpile 범위에 포함되도록 해야 한다. axios는 내부적으로 Promise를 사용하는 라이브러리인데, babel-plugin-transform-runtime은 Promise 전역 객체를 생성하지 않으므로 에러가 발생한다.
@babel/polyfill과 달리 필요한 부분에만 polyfill을 적용하기 때문에 bundle size 측면에서 이점이 있으나, 개발자가 많은 부분을 신경 써야 한다.
위 코드는 SoYoung210/test-polyfill-babel-transform-runtime 에서 테스트해볼 수 있다.
@babel/preset-env
core-js-compat을 디펜던시로 가지고 있고, babelrc에 설정된 target 값을 보고 core-js-compat/data를 이용해 필요한 polyfill만 로드한다. 명시된 target에서 지원되지 않는 JS 문법을 확인하여 @babel/plugin-*를 추가 해주는 방식이다. (Code)
useBuiltIns
useBuiltIns 옵션은 어떤 방식으로 polyfill을 넣어줄지 설정하는 옵션이다. 기본값은 false이므로 이 값을 설정하지 않으면 polyfill이 추가되지 않는다.
useBuiltIns: entry
// index.js
import 'core-js';transpile 하는 시작점에 import된 core-js모듈과 regenerator-runtime모듈을 babelrc에서 지정한 target에 맞게 변경한다.
// modern browsermodule.exports = {
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env", {
"targets": ">= 0.25%, not dead",
"useBuiltIns": "entry",
"corejs":3
}
]
]
}
// include IE10module.exports = {
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env", {
"targets": ">= 0.25%, not dead, ie >= 10",
"useBuiltIns": "entry",
"corejs":3
}
]
]
}ie >=10설정에는 es/object.set-prototype-of polyfill이 추가된다.
// modern browser
require("core-js/modules/es.array-buffer.is-view");
// include IE10
+ require("core-js/modules/es.object.set-prototype-of");target이 매우 구형 브라우저일 경우 과도한 polyfill이 추가되어 최신 브라우저에서도 크기가 큰 bundle file을 로드하게 되는 낭비가 발생할 수 있다.
test-polyfill/babel-preset-env 에서 target에 IE ≥ 10이 포함되어 있는 번들과 그렇지 않은 번들의 차이를 직접 확인할 수 있다.
useBuiltIns: usage
실제 코드에서 사용하는 polyfill만 import 하는 설정이다.
test-polyfill/babel-preset-env 에서 npm run build:modern:usage를 수행하면 아래와 같은 결과를 확인할 수 있다.
// Input
new Set([1,2,3])
var a = new Promise();
// Output
require("core-js/modules/es.array.iterator");
require("core-js/modules/es.object.to-string");
require("core-js/modules/es.promise");
require("core-js/modules/es.set");
require("core-js/modules/es.string.iterator");
require("core-js/modules/web.dom-collections.iterator");usage옵션은 사용하는 코드만 polyfill 대상으로 보기 때문에, 사용하는 node_modules의 dependency에서 polyfill이 적용되지 않은 코드가 있다면 에러가 발생할 수 있다.
또, 아래와 같은 코드에서 babel은 fooArrayOrObject가 string 인지 array 인지 판단할 수 없기 때문에 두 가지 polyfill을 모두 import 한다.
// Before
import { fooArrayOrObject } from './test';
console.log(fooArrayOrObject.includes());
// After
require("core-js/modules/es.array.includes");
require("core-js/modules/es.string.includes");
var _test = require("./test");
console.log(_test.fooArrayOrObject.includes());polyfill.io
polyfill.io service는 요청하는 브라우저의 User-Agent를 확인하여 필요한 polyfill만 추가할 수 있는 서비스이다. 지원되는 브라우저는 polyfill.io 페이지에서 확인할 수 있는데, IE 10이하는 지원하지 않는다.
User-Agent는 polyfill-useragent-normaliser를 통해 확인하고, getPolyfillString 함수를 통해 필요한 polyfill을 모두 생성한다.
polyfill-library에서
npm run test-node를 수행하여 다음과 같은 script가 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.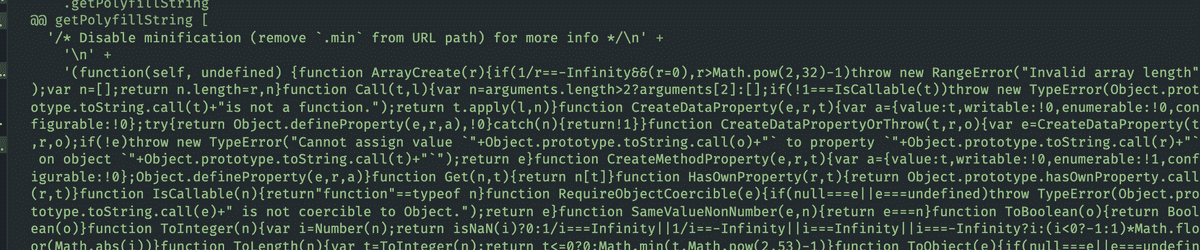
Usage
기본 설정으로 사용한다면 html 파일에 아래 script tag를 추가해 주면 된다.
<head>
<script src="https://polyfill.io/v3/polyfill.min.js?features=default"></script>
</head>polyfill-library는 전역 객체를 수정하는 방식이다.
// https://github.com/Financial-Times/polyfill-library/blob/master/polyfills/Array/isArray/polyfill.js
CreateMethodProperty(Array, 'isArray', function isArray(arg) { return IsArray(arg);
});
// https://github.com/Financial-Times/polyfill-library/blob/master/polyfills/_ESAbstract/CreateMethodProperty/polyfill.js
function CreateMethodProperty(O, P, V) { // eslint-disable-line no-unused-vars
var newDesc = {
value: V,
writable: true,
enumerable: false,
configurable: true
};
Object.defineProperty(O, P, newDesc);}Options
https://polyfill.io/v3/polyfill.min.js?features=default이렇게 default 값으로 사용할 경우 내부에 정의된 aliases.json을 참고하여 필요한 polyfill 목록을 자동으로 추가한다.
default 옵션에 어떤 polyfill이 정의되어 있는지 정리한 문서를 찾지 못하였는데, polyfill-library에서
npm run test-polyfills명령어를 통해 생성되는 polyfills/_dist/aliases.json 파일을 참고했다.
"default":
[
"Array.from","Array.isArray","Array.of","Array.prototype.every",
"Array.prototype.fill","Array.prototype.filter","Array.prototype.forEach",
....
]특정 기능만 사용하고 싶다면 feature 파라미터로, 제외하고 싶은 polyfill이 있다면 excludes로 명시해 주면 된다.
https://cdn.polyfill.io/v3/polyfill.min.js
?features=fetch,IntersectionObserver&excludes=Documentpolyfill을 load 할 때 User Agent 값과 관계없이 항상 load 하도록 설정하고 싶다면 flags=always 옵션을 활성화하면 된다. flags=always로 요청할 때, 사용하고자 하는 polyfill이 브라우저에 구현되어 있는지 확인하는 옵션은 flags=always, gated이다.
https://cdn.polyfill.io/v2/polyfill.min.js
?features=fetch,IntersectionObserver&
flags=always,gated모든 옵션에 대한 정보는 API Reference에서 확인할 수 있고, 옵션에 따라 쿼리파라미터를 자동으로 생성해주는 url-builder 를 활용하면 좀더 편하게 쓸 수 있다.
Security
쿼리 파라미터로 옵션을 명시하는 방식이다 보니, XSS 공격에 대한 취약점이 우려될 수 있다. polyfill.io는 옵션 값들을 escape 처리하여 공격을 방지하고 있다. script 문자인 < 는 <, > 는 > 로 escape하여 코드상에 script 태그 등이 있더라도 HTML로 해석되지 않도록 한다.
자세한 내용은 이 글에 정리되어 있다.
polyfill-service는 이 커밋을 통해 XSS 공격 방지 기능을 추가했고, polyfill-service 3.1.2 version부터 대응되어 있다.
자체 polyfill.io 서버 구축하기
polyfill.io 서버가 항상 안정적이라는 보장이 없기 때문에 production에서 polyfill.io를 직접 사용하는 방식은 부담스러울 수 있다. polyfill-library를 self-hosted server로 운영하면 이런 부담을 줄일 수 있다.
Docker를 사용해 쉽게 자체 polyfill-service를 구축할 수 있다.
FROM node:12.18.0-alpine
RUN apk add --no-cache --update bash
RUN apk add --no-cache --update --virtual build git python make gcc g++
WORKDIR /polyfill
# 맞는 버전 명시
ARG POLYFILL_TAG='v4.8.1'
ARG NODE_ENV='production'
RUN \
git clone https://github.com/Financial-Times/polyfill-service . && \
git checkout ${POLYFILL_TAG} && \
rm -rf .git && \
yarn install && \
sed -i.bak -e 's,^node,exec node,' start_server.sh && \
mv start_server.sh /bin/ && \
chmod a+x /bin/start_server.sh && \
apk del build
ENV PORT 8801
EXPOSE ${PORT}
CMD ["/bin/start_server.sh", "server/index.js"]라이브러리 제작자라면?
polyfill을 처리하는 방식을 정리하고 나니, 라이브러리를 개발할 때 polyfill 설정은 어떻게 적용하는 것이 가장 좋은 방법인지 의문이 들었다.
polyfill의 책임은 라이브러리일까, 아니면 Application 레벨일까에 관해 논의하던 GitHub Issue에서 webpack 메인테이너 sokra는 다음과 같이 말했다.
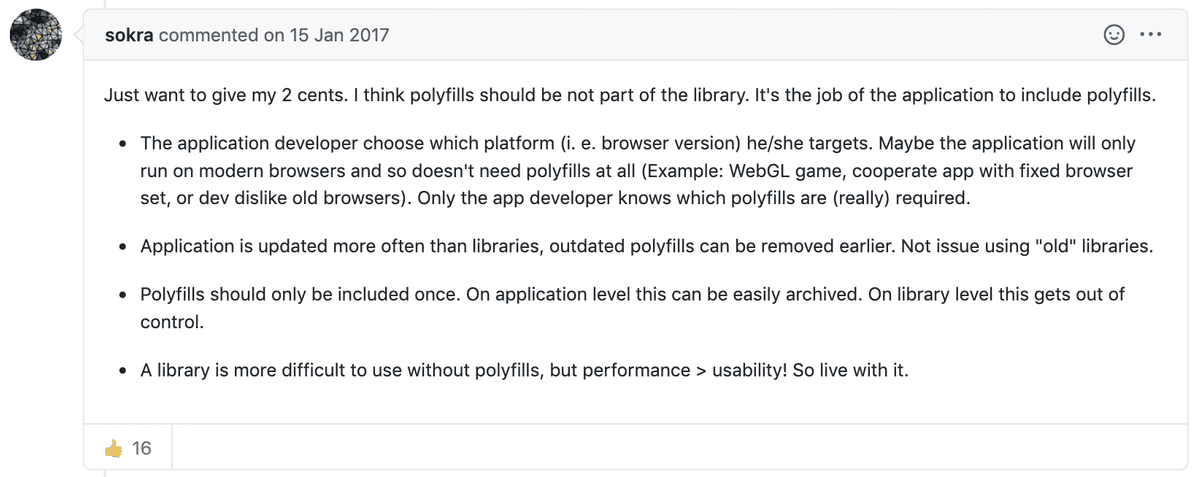
polyfill필요 여부는 Application레벨에서는 쉽게 제어할 수 있지만, 라이브러리 레벨에서는 그렇지 않다.
때문에, 많은 사람들이 polyfill의 책임을 Application으로 이양하고 polyfill이 필요한 부분에 대해 힌트를 제공하는 방식을 긍정적으로 이야기 했다.
마무리
babel은 polyfill을 추가하는 가장 쉽고 확실한 방법이지만 polyfill이 필요없는 최신 브라우저에서는 불필요하게 번들 사이즈가 증가한다.
SPA에서 신경써야 하는 부분 중 하나인 ‘번들 사이즈’에 고민이 있다면, User-Agent기반으로 필요한 polyfill만 로드하는 방식인 polyfill.io도 선택지가 될 수 있다.
다만, polyfill.io를 선택할 때는 추가적인 서버 관리 비용에 대한 고려와 core-js maintainer “zloirock”가 언급한 부정확한 polyfill이슈는 없는지 충분한 테스트가 필요할것 같다.
References
- https://programmingsummaries.tistory.com/
- https://github.com/babel/babel/blob/master/packages/babel-polyfill/package.json
- https://github.com/zloirock/core-js
- https://3perf.com/blog/polyfills/
- https://babeljs.io/docs/en/babel-plugin-transform-runtime
- https://github.com/Financial-Times/polyfill-library
- https://slides.com/odyss/deck-8
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8GcVBTBI4Ew&list=PLZl3coZhX98oeg76bUDTagfySnBJin3FE&index=12
- https://snyk.io/vuln/npm:polyfill-service:20160126
- https://github.com/3YOURMIND/js-polyfill-docker