Rollup.js 환경설정
January 17, 2021

이 글에서는 디자인 시스템 개발 환경을 구축하는 단계에서 rollup.js과 라이브러리 설정에 관한 내용을 정리하는 글입니다. 하지만 환경설정에 대한 튜토리얼은 아니기 때문에 필요한 모든 내용을 다루지는 않습니다.
이 글에서 구성한 환경 구축 내용만 보고 싶으시다면 @soyoung/design-system-config 에서 보실 수 있습니다.
Table Of Contents
Rollup.js
Rollup.js은 webpack이나 parcel과 같이 크고 복잡한 코드의 모듈(파일)을 라이브러리나 어플리케이션으로 만들어주는 번들러입니다.
Config
rollup.js에는 많은 플러그인과 옵션을 설정할 수 있습니다. es(ES module) 형식과 cjs(Common JS)형식을 지원하는 rollup.config.js 는 다음과 같이 구성할 수 있습니다.
// rollup.config.js
const inputSrc = [
['./src/index.ts', 'es'],
['./src/index.ts', 'cjs'],
];
export default inputSrc
.map(([input, format]) => {
return {
input,
output: {
dir: 'dist',
format,
},
plugins: [],
};
});필수 플러그인을 추가합니다.
import babel from '@rollup/plugin-babel';
import commonjs from '@rollup/plugin-commonjs';
import { nodeResolve } from '@rollup/plugin-node-resolve';
import peerDepsExternal from 'rollup-plugin-peer-deps-external';
import postcss from 'rollup-plugin-postcss';
import { terser } from 'rollup-plugin-terser';
export default inputSrc
.map(([input, format]) => {
return {
input,
output: {
dir: `dist2/${format}`,
format,
exports: 'auto',
},
external: [/@babel\/runtime/],
// 추후 설명
preserveModules: format === 'cjs',
plugins: [
babel({
babelHelpers: 'runtime',
exclude: 'node_modules/**',
extensions,
}),
nodeResolve({
extensions,
}),
// https://velog.io/@peterkimzz/rollup-%ED%94%8C%EB%9F%AC%EA%B7%B8%EC%9D%B8
// CommonJS 로 작성된 모듈들을 ES6 바꾸어서 rollup이 해석할 수 있게 도와줍니다.
commonjs({
extensions: [...extensions, '.js'],
}),
peerDepsExternal(),
postcss({
plugins: [],
}),
terser(),
],
};
});- @rollup/plugin-babel: rollup에서 babel을 사용할 수 있게 해주는 플러그인입니다.
- @rollup/plugin-node-resolve: 라이브러리 내에서 써드파티 모듈(package.json내의 dependencies)을 사용하는 용도로 사용하며, js이외의 확장자(ts, tsx) 파일을 불러오기 위해서도 사용합니다. 외부 모듈에 대한 Tree Shaking또한 지원합니다.
-
@rollup/plugin-commonjs: CommonJS 형태로 이루어진 모듈의 코드를 ES6로 변환하여 결과물에 포함될 수 있게 해줍니다. 예시 프로젝트에서
commonjs플러그인을 제외하고 빌드 시 아래와 같은 에러를 확인할 수 있습니다.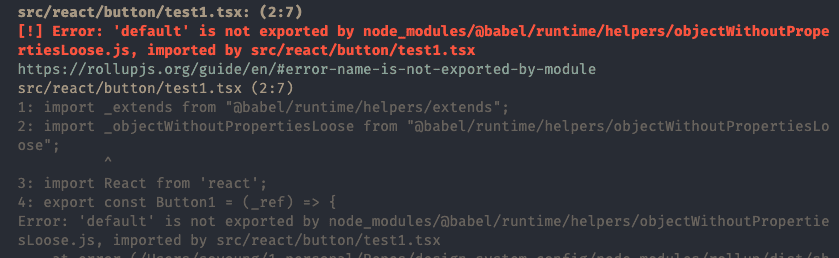
-
rollup-plugin-peer-deps-external: package.json에 명시된
peerDependency모듈을 라이브러리 번들 결과물에서 제외합니다.// peer-deps-external없을 때의 번들에서의 모듈 참조 import { someThing } from '../../../node_modules/some' // peer-deps-external추가 시 아래와 같이 유지되고 사용되는 곳에서의 node_modules참조 import { someThing } from 'some' - rollup-plugin-terser: 번들 결과물을 minify해줍니다.
preserveModules
rollup.js의 preserveModules옵션을 true로 지정할 경우 번들 결과물의 폴더 구조를 유지할 수 있습니다.
- 기본값 false일 경우 결과물은 단일 파일로 생성됨
공식문서에 따르면, 이 값은 Tree shaking지원에 영향을 주지 않습니다. cjs 혹은 amd 포맷에서 특정 요소만 사용할 시 모든 코드를 import하지 않는다는 차이점이 있습니다.
⚠️ 공식문서에서는 ’preserveModule: true 설정도 tree shaking을 지원한다.’ 라고 명시되어 있습니다.
하지만,preserveModules: true로 설정할 경우 한 파일에서 treeshake가 실패하더라도 다른 파일까지 실패하지 않도록 영향범위를 최소화해주기 때문에, 실제 번들에서 테스트해 보시는 것을 추천합니다. (관련 이슈: webpack - tree shaking not working es module library)
// Before
const module = require('@soyoung210/design-system-config')
render(module.Card);
// After
const Card = require('@soyoung210/design-system-config/dist/cjs/react/card/card3D');
render(Card);cjs는 별도 tree shaking이 지원되지 않기 때문에, 단일 파일에서 모든 코드를 포함하고 있으면 어플리케이션의 번들 사이즈가 커질 수 있습니다.
📝 이 옵션의 탄생 배경은 “Ember.js”를 사용하는 어플리케이션에서의 트리 쉐이킹을 지원하기 위해 만들어진 것입니다. (관련 PR)
babel
rollup.config.js에서의 babel을 아래와 같이 설정해주었습니다.
babel({
babelHelpers: 'runtime',
exclude: 'node_modules/**',
extensions,
}),@rollup/plugin-babel의 옵션 중 babelHelpers 는 4가지 값을 가질 수 있습니다.
-
runtime: 공식 document에서 ‘라이브러리 빌드 시’ 추천하는 옵션입니다. @babel/plugin-transform-runtime 과 함께 사용해야 하며, 라이브러리의 디펜던시로 @babel/rutime을 명시해야 합니다.
@babel/plugin-transform-runtime에 대해 궁금하다면 공식문서와 you don’k know polyfill - babel/plugin-transform-runtime글을 참고해주세요.⚠️ 이 옵션을 사용할 경우
external: [/@babel\/runtime/]을 추가해야 합니다. - bundled: babel helper함수들이 번들 결과물에 포함되도록 하는 옵션입니다. 주로 어플리케이션 개발 시 사용합니다.
- external: 이 옵션은 주의해서 사용할 것을 당부하고 있습니다. 내부 helper function을 자동으로 생성하는 것이 아니라, 커스텀하게 설정할 수 있는 옵션입니다. 이 옵션에 대한 자세한 내용은 이 글 을 참고해주세요.
- inline: 이 옵션은 권장되지 않습니다. helper function이 각 파일에 중복적으로 생성되기 때문입니다.
4가지 옵션 중 runtime 옵션과 bundled 옵션에 대해 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
빌드 테스트에 사용되는 예시 코드는 react와 css만을 사용해 만든 Button1컴포넌트와 react-spring을 사용한 Card컴포넌트로 구성되어 있습니다.
babelHelpers: bundled
export default [
// ...
plugins: [
babel({
babelHelpers: 'bundled', // default value
exclude: 'node_modules/**',
extensions,
})
]
]이렇게 설정할 경우, 번들 결과물에 babel helper function이 포함됩니다. 번들 결과물은 다음과 같습니다.
function _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose(source, excluded) {
/* 생략 */
}
const Button1 = (_ref) => {
let {
children
} = _ref,
props = _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose(_ref, ["children"]);_objectWithoutPropertiesLoose함수가 파일에 포함된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
babelHelpers: bundled + external: [/@babel/runtime/]
export default [
// ...
external: [/@babel\/runtime/],
plugins: [
babel({
babelHelpers: 'bundled',
exclude: 'node_modules/**',
extensions,
})
]이 옵션을 같이 사용할 경우 어떻게 될까요?
import _extends$1 from '@babel/runtime/helpers/esm/extends';
import _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose$1 from '@babel/runtime/helpers/esm/objectWithoutPropertiesLoose';
function _extends() {
/* 생략 */
}
function _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose(source, excluded) {
/* 생략 */
}_objectWithoutPropertiesLoose$1은 @babel/runtime모듈에서 참조하도록 변경되었고, _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose은 내부에 생성되었습니다.
_objectWithoutPropertiesLoose$1 은 node_modules/react-spring에서 참조하고 있습니다. 외부 모듈(이 글에서의 예시 프로젝트에서 포함 한react-spring)에서 참조하는 @babel/runtime 은 ‘외부’로 유지되었습니다.
반면, Button1 에서 필요한 @babel/runtime의 모듈은 번들 내부에 생성되었습니다.
babelHelpers: runtime + external: [/@babel/runtime/]
export default [
// ...
external: [/@babel\/runtime/],
plugins: [
babel({
babelHelpers: 'runtime',
exclude: 'node_modules/**',
extensions,
})
]
]@babel/runtime에 대한 모든 참조가 외부로 변경됩니다. babel config에 @babel/transform-runtime가 반드시 포함되어 있어야 합니다.
import _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose from '@babel/runtime/helpers/objectWithoutPropertiesLoose';
const Button1 = (_ref) => {
let {
children
} = _ref,
props = _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose(_ref, ["children"]);_objectWithoutPropertiesLoose 함수 구현이 내부에 생성되는 것이 아니라 외부 모듈을 참조하도록 변경되었습니다.
babelHelpers: runtime
export default [
// ...
// external: [/@babel\/runtime/],
plugins: [
babel({
babelHelpers: 'runtime',
exclude: 'node_modules/**',
extensions,
})
]
]공식문서에서 가이드 하고있는 external: [/@babel\/runtime/]설정을 제외하고 빌드해보면 babelHelpers: 'bundled'와 같은 결과임을 확인할 수 있습니다.
function _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose(source, excluded) {
/* 생략 */
return target;
}
const Button1 = (_ref) => {
let {
children
} = _ref,
props = _objectWithoutPropertiesLoose(_ref, ["children"]);따라서, runtime 옵션 적용시 external 설정을 반드시 해주어야 합니다.
Tree Shaking Result
라이브러리에서 중요한 것 중 하나는 Tree Shaking입니다. 유저가 라이브러리 코드 중 일부만 사용했는데, 전체가 번들 결과물에 포함되어 불필요하게 용량을 증가시킨다면 아무리 잘 만든 라이브러리라도 선뜻 사용하기 어려울 것입니다.
하나의 파일로 번들링 될 경우 Bundle Analyzer에서 결과를 확인하기 어려운데, 이 경우 어플리케이션의 최종 번들 결과물을 확인해보면 Tree Shaking적용 여부를 알 수 있습니다.
@soyoung210/design-system-config를 install하여 결과를 확인하였습니다.
Card컴포넌트를 포함했을 때
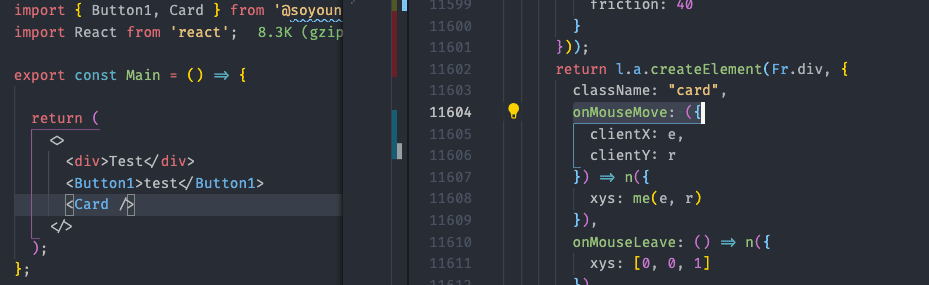
Card컴포넌트(함수)를 이루는 onMouseMove와 관련 코드들이 최종 번들에 포함되었습니다.
Card컴포넌트를 포함하지 않았을 때
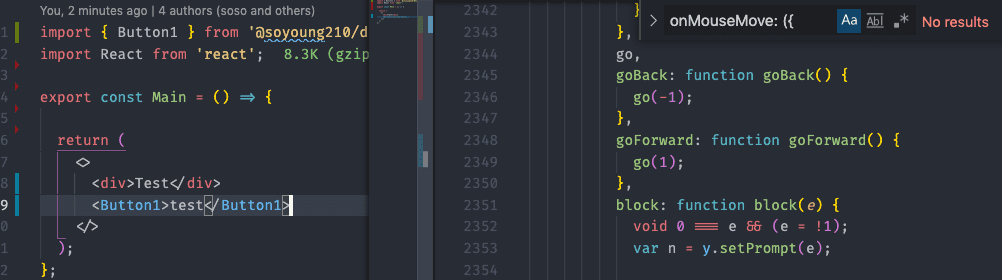
Card 컴포넌트를 이루는 코드는 사라졌지만, Card 컴포넌트에서 사용한 react-spring 관련 코드들은 포함되었습니다. 이는 react-spring의 이슈 같기도 하지만, preserverModules에서 언급한 하나의 파일에서 tree shake가 실패하여 전체에 영향을 주는 예시입니다.
Tree Shaking에 관해 자세한 내용이 궁금하시다면 이 글을 읽어보시는 것을 추천드립니다.
Why not Webpack?
webpack 역시 JavaScript Bundler입니다. 기본적으로 같은 기능을 수행하므로 webpack을 사용할 수도 있지만, 라이브러리 Bundler로 webpack보다 rollup을 선택하는 몇 가지 이유가 있습니다.
webpack은 ESM형태로 번들이 불가능합니다.
Tree Shaking조건은 번들링 된 결과물이 ESM형태여야 하지만, Webpack은 ESM형태로 번들할 수 없습니다. 이에 반해, Rollup은 ESM형태로 번들링하는 것이 가능합니다. 🔔 Webpack5에서 ESM형태의 지원을 계획하고 있으나, 2021.01.10 기준 아직 실험단계입니다.
또, 같은 결과물을 번들링 했을 때 Rollup.js는 22KB / Webpack은 29KB로 webpack으로 번들링했을 때의 파일크기가 더 큽니다. 이 내용에 대해 더 자세히 알고 싶으시다면 Webpack에서 Rollup 전환기를 참고해 주세요.
Why not babel cli?
모듈을 번들링하지 않고 babel로 transpile만 하도록 설정할 수도 있습니다. chakra-ui, react-query(esm)등 많은 오픈소스에서 사용하고 있는 방식입니다.
- 장점: 번들러 관련 환경설정이 필요없고, react-query에서는 이런 이유로 번들링하지 않는 설정을 유지합니다.
- 단점: babel은 번들러가 아니기 때문에 트랜스파일링 외의 작업을 수행할 수 없고, 아래 상황들에 대응할 수 없습니다.
상황 1: 내부 디펜던시를 사용하는 경우
// babel cli
import { animated, useSpring } from 'react-spring';
export function Card() {
return /*#__PURE__*/React.createElement(animated.div, { ... })
}
// rollup
import { useSpring, animated as extendedAnimated } from '../../../node_modules/react-spring/web.js';react-spring이 라이브러리 내부 디펜던시로 취급되는 것을 바랄 경우 대응이 어렵습니다. babel을 통한 변환은 import { .. } from 'raect-spring구문을 따로 변환하지 않으므로 사용하는 외부 디펜던시는 모두 peerDependencies로 다뤄져야 합니다.
상황 2: custom style sheet
컴포넌트 내에서 style sheet를 사용하는 경우. 번들러는 스타일 파일을 해석해서 적절히 변환하지만, babel은 그렇지 않습니다.
// babel cli
import './styles.css';
import React from 'react';
// rollup
import React from 'react';
import './styles.css.js';
// rollup이 style sheet를 처리하는 방식 styles.css.js
import styleInject from '../../../node_modules/style-inject/dist/style-inject.es.js';
var css_248z = ".card {\n width: 45ch;}\n";
styleInject(css_248z);
export default css_248z;package.json
번들러를 통해 cjs(or umd), esm 등 다양한 형식을 지원한다면, package.json에 맞는 포맷을 연결해주어야 합니다.
- module:
module필드는 ES6 모듈의 시작점 위치입니다. - main: 패키지를 설치한 뒤
require('foo')를 실행했을 때 반환될 파일의 위치입니다.
두 가지 옵션을 함께 명시하면 rollup이나 webpack등의 번들러를 사용할 때는 module필드를 참조하고, ES6를 사용할 수 없는 Jest환경 등에서는 main필드의 파일을 참조하게 됩니다.
TypeScript
TypeScript코드를 다룰 때는 JS 변환과정을 추가해야 하고, type definition파일을 생성해야 합니다.
JS 변환은 앞서 설정한 @rollup/plugin-babel혹은 rollup-plugin-typescript2를 통해 수행할 수 있고, type defnition파일은 tsc를 통해 간단하게 수행할 수 있습니다. 먼저, tsc를 통한 type defnition생성에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
💡 rollup에서 공식지원하는 typescript plugin은 @rollup/plugin-typescirpt 이나, 밑에서 소개할 이슈로 본 글에서는 rollup-plugin-typescript2를 소개합니다.
tsc
우선, tsconfig를 아래와 같이 설정해 줍니다. (반드시 아래 설정과 일치할 필요는 없습니다.)
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ESNext",
"module": "ESNext",
"lib": ["dom", "esnext"],
"strict": true,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
"moduleResolution": "Node",
"suppressImplicitAnyIndexErrors": true,
"noImplicitAny": true,
"strictFunctionTypes": true,
"strictNullChecks": true,
"strictPropertyInitialization": true,
"jsx": "react",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["src/**/*"]
}package.json을 일부 수정하여 build 시 type definition파일이 함께 생성되도록 합니다.
"scripts": {
"build:rollup": "rimraf ./dist2 && rollup -c ./scripts/rollup/rollup.config.js && npm run build:types2",
"build:types2": "tsc --emitDeclarationOnly --declaration --declarationDir dist2/types"
},rollup-plugin-typescript2
Rollup과 TypeScript를 함께 사용할 때, rollup-plugin-typescript2를 사용하거나 @babel/preset-typescript(w. @rollup/plugin-babel)을 사용할 수 있습니다.
이 두 가지 방식의 주요 차이점은 TypeScript해석에 대한 접근방식입니다.
- rollup-plugin-typescript2: 내부적으로
tsc를 완벽하게 지원합니다. - @babel/preset-env: TypeScript를 JavaScript로 transpile하지만, type check기능은 수행하지 않습니다. (참고 - @babel/plugin-transform-typescript 공식문서)
어느 쪽을 선택해도 큰 차이는 없습니다. 이 글에서 다루는 프로젝트는 babel을 transpiler로 사용하고 tsc로 type definition파일만 생성하는 전략을 가져가고 있어 @rollup/plugin-babel만 사용했습니다.
📝: rollup-plugin-typescript2는 rollup의 공식 TypeScript도구인
@rollup/plugin-typescript에서 TypeScript compile error 기능을 포함하기 위해 fork하여 제작된 라이브러리입니다. TypeScript의 강력한 기능을 사용할 수 있지만, 빌드 속도가 아주 느리다는 이슈가 있습니다.
⚠️ Tree Shaking과정에서
/*#__PURE__ */annotation이 있으면 sideEffect가 없다고 판단하여 제거하는데, babel은 v7부터 pure annotation을 지원하지만, TypeScript는 아직 지원하지 않습니다. 번들 결과물에서 pure annotation포함 여부도 확인해보는 것이 좋습니다.
마무리
Rollup.js 설정파일을 구성하며 궁금했던 부분을 조사하고 정리해봤습니다. 이 글이 Rollup.js와 친숙하지 않으셨던 분께는 도움이 되셨길 바라고, 글에 부족한 내용이나 수정이 필요한 부분이 있다면 코멘트로 남겨주시면 감사하겠습니다.